Elliptic Curve Cryptography
Elliptic Curve
Point Addition
-
The point has to be reflected on the x-axis to keep the associactivity of addition
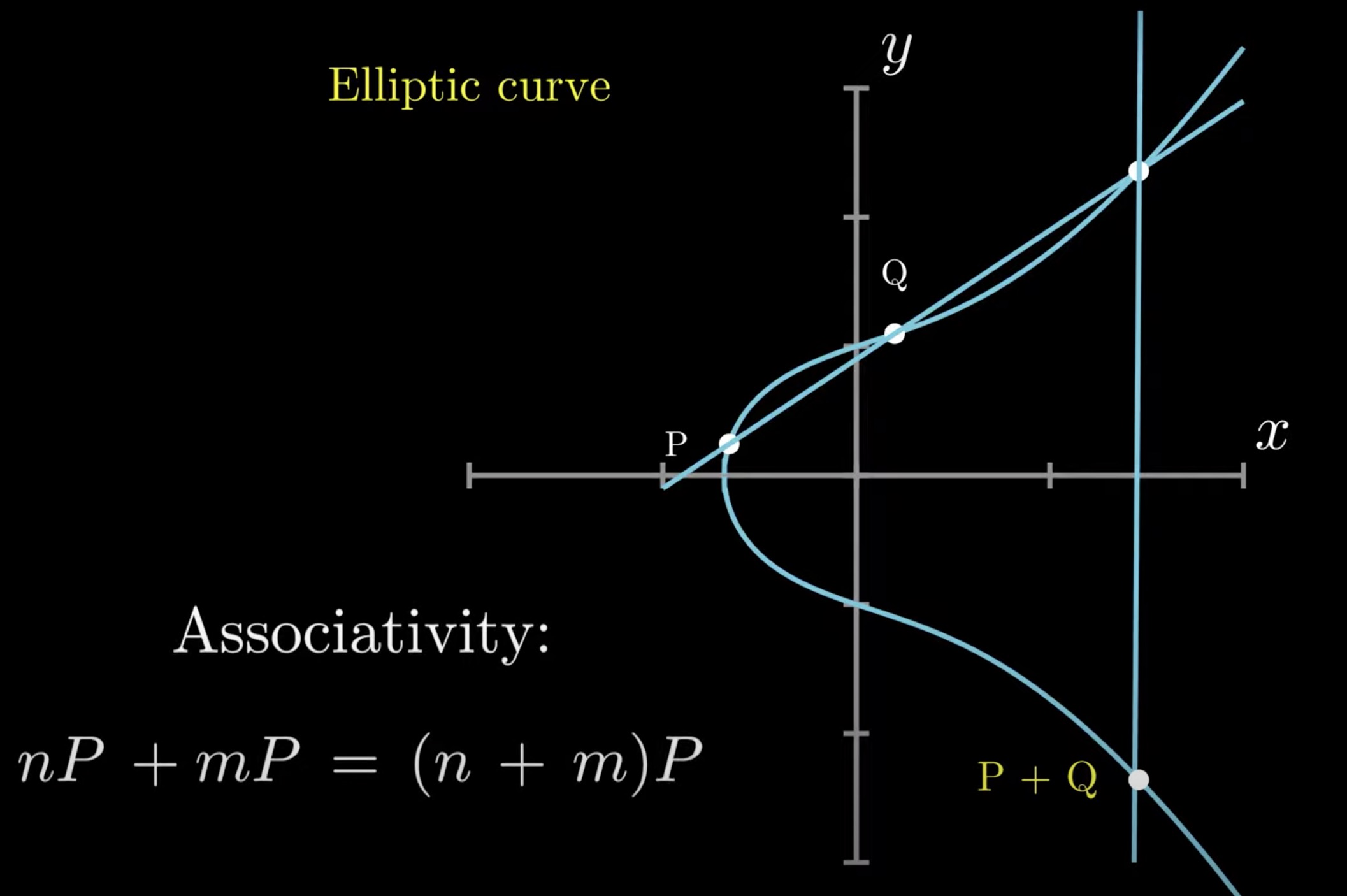
Point Doubling
-
Naturally consider the tangent line
Elliptic curve cryptography
-
To guess the private key is super super hard
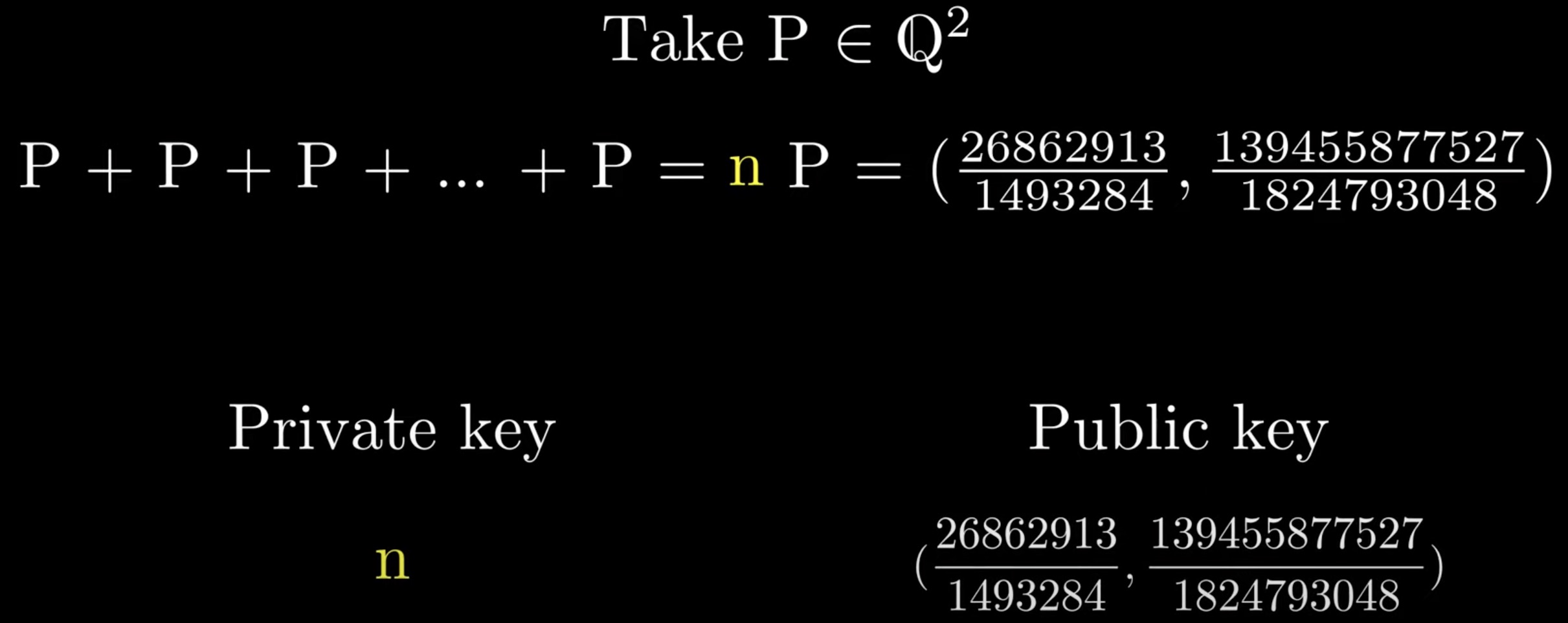
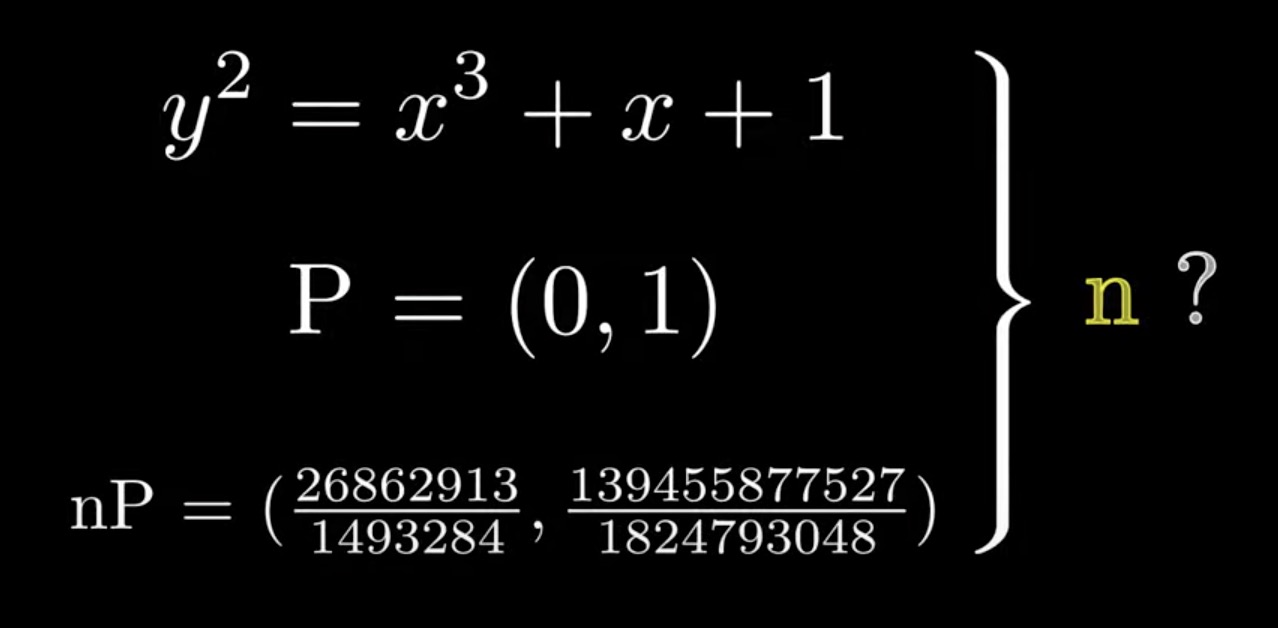
The problem of elliptic curve over real numbers
-
The consecutive points of curve with the beginning point are as follows. For just few steps, the numerator or denominator are going to be too large for computers

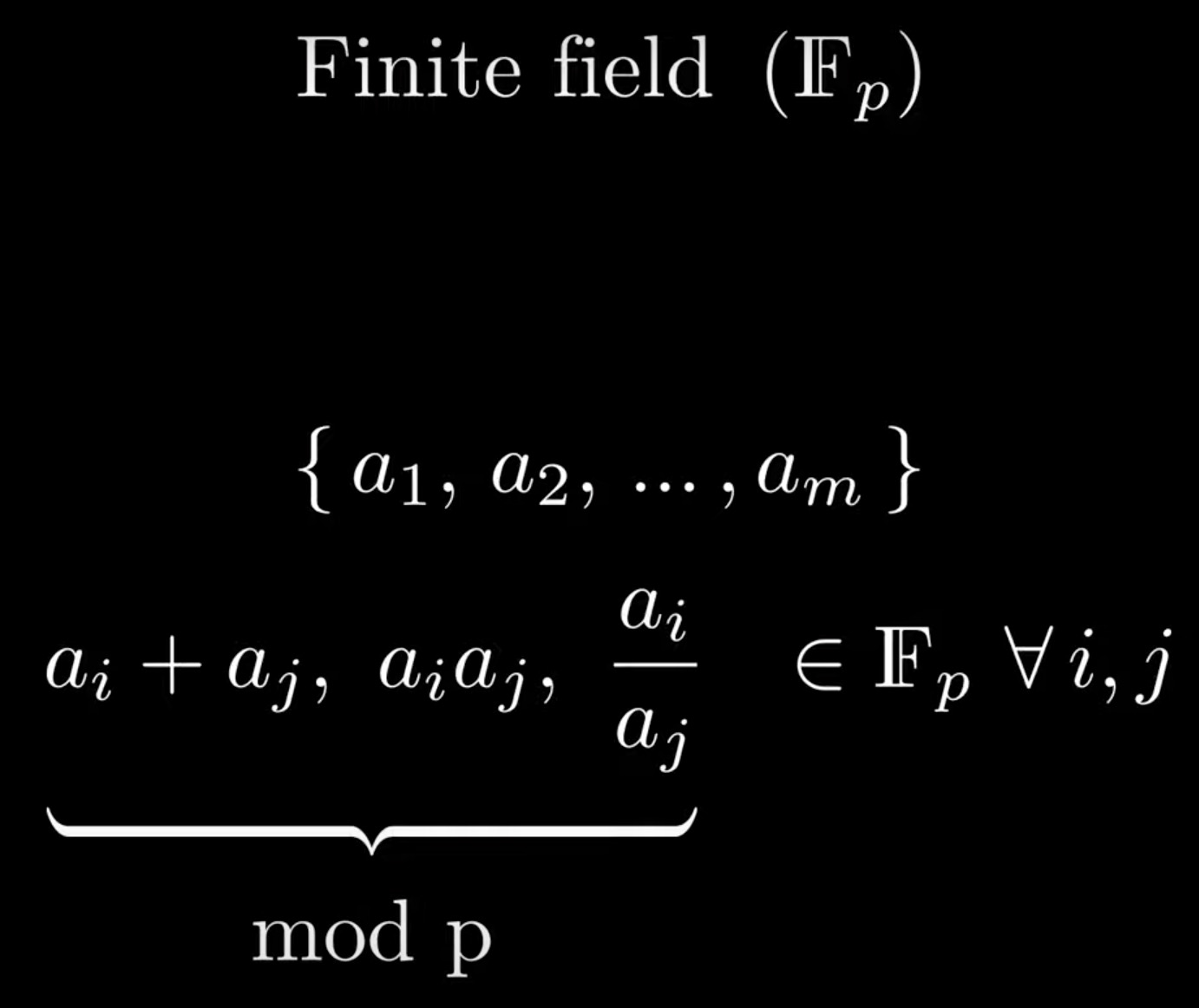
Elliptic curve over finite field
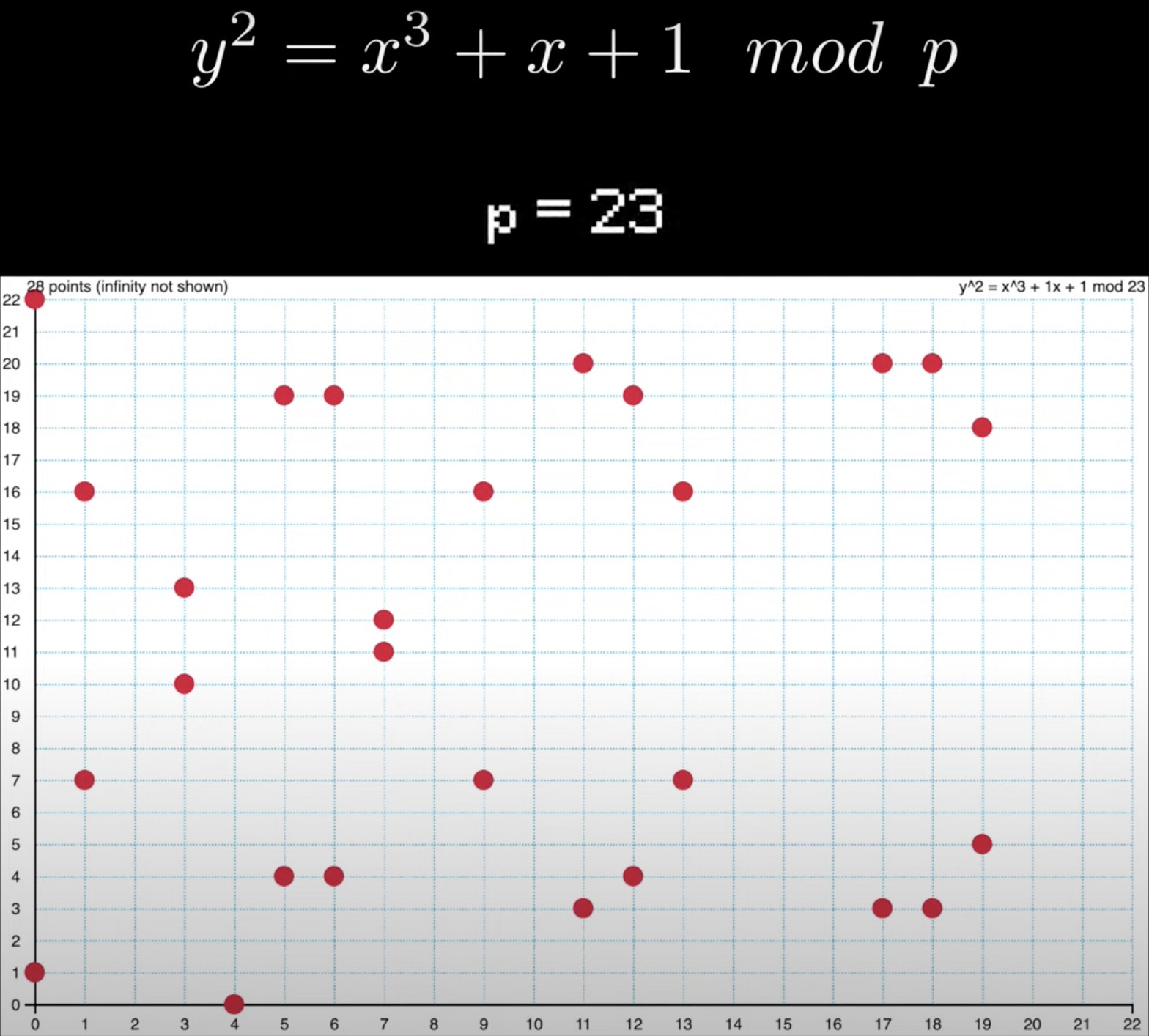
How to calculate the public key
Double-and-add algorithm
-
Suppose private key and given the start point . The steps of calculating the public key is as follows. What is supposed to be mentioned is that the intermidiate resutl of each step has been calculated

Point addition
- Take secp256k1 curve as an example:
-
According to the Vieta’s formulas
then reflect
where , .
Point doubling
-
According to the point addition section, , and
Since , and are modular inverse for each other with modulo .
Elliptic curve for bitcoin
-
The curve equation, prime order of the elliptic curve and the x-coordinate of the base point are as follows.
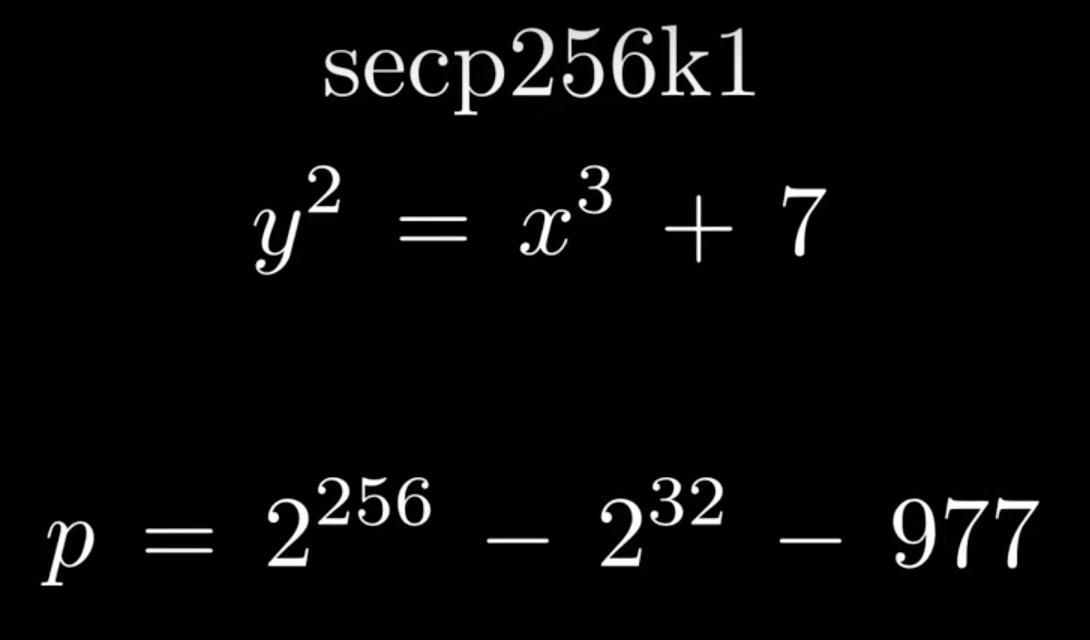

ECDSA (Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm)
-
Sign (how to calculate signature )
- given (private key), (message hash), (base point)
- choose a random number , derive point
-
Send transaction
- given
- dervive and with and curve ( curve is symmetric)
- determine one of and with v, then derive
- dervive (public key) according
- derive
fromaddress according - check balance and nonce of
fromaddress - send transaction
-
Verify signature
- given
- derive according
- check
-
Signature malleability
- given , where
- notice that
- so according to
- so
-
RFC-6979
- HMAC
Given and curve, two points and can be derived, where . It is known that is a big prime number which is odd. So for and , one is odd and the other is even. Given , the correct y-coordinate is determmined.
If any of is corrupted, a different
fromaddress will be derived. Usually, the address has no balance and the transaction will be rejected.